If you are using the full-text search, you may encounter some special behavior. Like adding an account named „STILL“. If you try to find the account with enabled full-text search, you won’t find it. With disabled full-text search, the account can be found with the quick find.
I was working with a Microsoft engineer on this case and we found the solution:
First I used the “sql profiler” to get the sql statement:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
exec sp_executesql N'WITH __QuickFind__ as (select top 10001 [AccountId] from ( SELECT "account0".[Key] AS [AccountId] FROM ContainsTable([AccountBase], (Name, AccountNumber, EMailAddress1, Telephone1, Telephone2), @Name0) AS "account0") as [__QuickFindInternal__])select top 51 "account0".Name as "name" from Account as "account0" left outer join Workflow as "processidworkflowworkflowid" on ("account0".ProcessId = "processidworkflowworkflowid".WorkflowId) where [account0].[AccountId] in (select [AccountId] from [__QuickFind__]) and (((("account0".StateCode = @StateCode0)))) order by "account0".Name asc , "account0".AccountId asc',N'@StateCode0 int,@Name0 nvarchar(200)' ,@StateCode0=0,@Name0=N'((("STILL*" OR FORMSOF(FREETEXT, "STILL"))) OR ("STILL"))' |
The statement looks good. So I check the catalog:
- Check the Full-Text Catalog:
In order for the quick find to work, the tables for the entities that you have configured in CRM have to be present on the Full-Text Catalog:
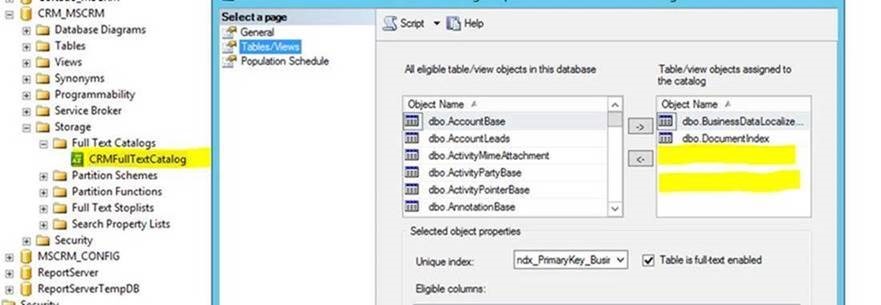 Then, to the Full text catalog General page and check on its status. It should be in “Idle”.
Then, to the Full text catalog General page and check on its status. It should be in “Idle”.
Depending on the result of the status and the Last Population Date we need to see if we need to Rebuild the catalog or not. - Check the Indexes that run in the quick find:The indexes that were already crawled and should be ready to be used in the Full-Text catalog and in the Quick find.
This query is used to see if the indexes are ready.
123456select OBJECT_NAME(i.object_id) as TableName, c.name as ColumnName, i.crawl_end_date as CrawlEndDate,i.crawl_start_date, i.has_crawl_completed, i.crawl_type_desc, *from sys.fulltext_indexes iinner join sys.fulltext_index_columns ic on i.object_id = ic.object_id and i.object_id = ic.object_idinner join sys.columns c on c.object_id = ic.object_id and c.column_id = ic.column_idorder by CrawlEndDate
If the “has_crawl_completed” Column has the value (1=complete), it should be ready. - Check if the indexes are being used:
123456789select ia.CreatedOn, Name, ei.IndexType, ia.IsSystemManaged,ia.IsQuickFindManaged, ia.State as IndexAttributeState, ei.State as EntityIndexState, *from indexattributes as iaINNER JOIN(select * from EntityIndex as ewhere e.indextype=9 -- FullText) as eion ia.IndexId=ei.IndexId
This query will let us see which indexes are being used by the Quick find. If the “State” column is at 2 they are being used.
All this was ok. So we checked the rebuild of the catalog:
|
1 2 |
SELECT fulltextcatalogproperty('CRMFullTextCatalog', 'ItemCount') SELECT fulltextcatalogproperty('CRMFullTextCatalog', 'IndexSize') |
Every time you activate “Quick Find”, this is what is happening in the background:
There are two maintenance jobs that are responsible for the quick find. These are the ScaleGroupOrganizationMaintenanceJobs (Type 15 and 61).
The ScalegroupOrganizationMaintenanceJob 15 is the IndexManagement job.
The ScalegroupOrganizationMaintenanceJob 61 is the CheckFullTextIndexColumnStatusOperation job.
To check if they are running or already ran, execute the following queries.
- Use this query to find your organization id:
123Use MSCRM_CONFIGselect FriendlyName, idfrom Organization - Execute the following queries (replacing [orgid] by the ID of your organization):
123456789Use MSCRM_CONFIGselect State, NextRunTime, LastRunTime, *from ScaleGroupOrganizationMaintenanceJobswhere operationtype = 15 and OrganizationId='[orgid]'Use MSCRM_CONFIGselect State, NextRunTime, LastRunTime, *from ScaleGroupOrganizationMaintenanceJobswhere operationtype = 61 and OrganizationId='[orgid]'
Check the LastRunTime and the NextRunTim. These jobs should run at least weekly. If they haven’t been run, we need to force them to run. - Force the jobs to run, if they haven’t. Be aware, that this may cause performance issues during execution, means that you should execute this not during the office hours.
1234567Use MSCRM_CONFIGupdate ScaleGroupOrganizationMaintenanceJobs set NextRunTime = GETUTCDATE()where operationtype = 15 and OrganizationId='[orgid]'Use MSCRM_CONFIGupdate ScaleGroupOrganizationMaintenanceJobs set NextRunTime = GETUTCDATE()where operationtype = 61 and OrganizationId='[orgid]'
In my case, all queries run correctly. Therefore the Microsoft engineer found the error. The SQL-server creates the catalog itself and therefore excludes some filling words like does, each, else, for, from, get, got and many more. To get the list of all “stopwords”, execute the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 |
To get a list of all words for English use the following query: SELECT * FROM sys.fulltext_system_stopwords WHERE language_id = 1033; |
Be aware, that each language has its own stopwords.
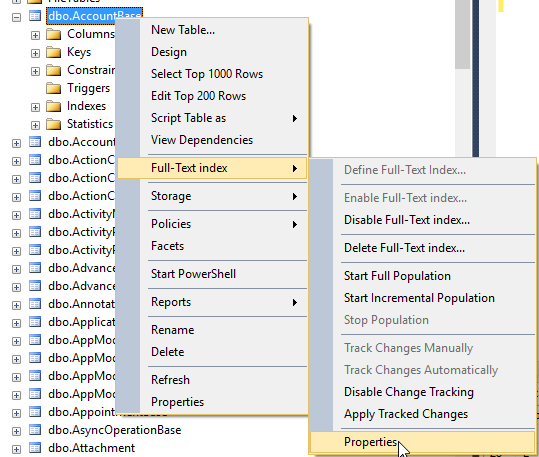
One possible solution is to disable the stopwords for specific entities, in my case for the account. Therefore, go to the table account, right-click and select the entry “Full-text index” and select properties.
Change the value of “Full-text Index Stoplist” to off. This will disable the stoplist only for the account-entity.
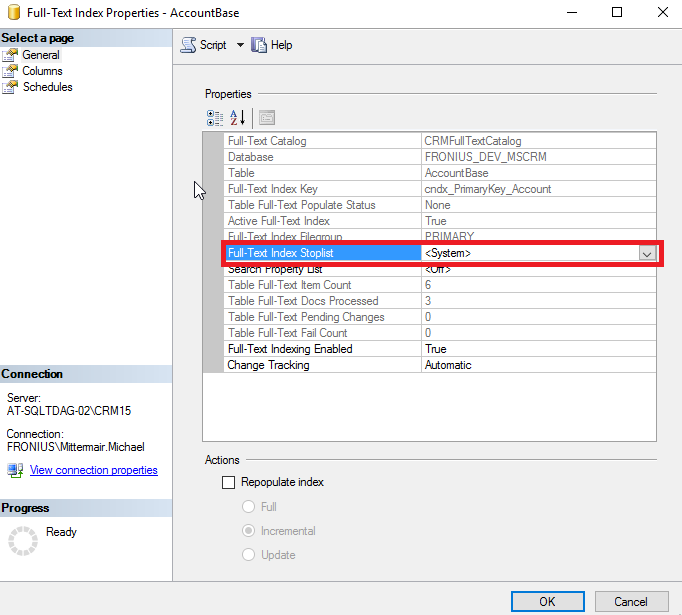
Based on the restrictions of Microsoft, this should be a supported change, as this is not a change of the schema:
Modifications to the physical schema of the database, other than adding or updating indexes. This includes any actions performed against the database without using the System Customization capabilities in the web application or using the metadata APIs that are described in this SDK documentation. Modifying tables, stored procedures, or views in the database is not supported. Adding tables, stored procedures, or views to the database is also not supported because of referential integrity or upgrade issues.